Note: the term “Life” here includes Biological life and Machine life. The creation of life relies on a succession of stages beginning with the formation of the universe. The widely accepted theory ( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_Bang) is that the universe was created some 13.8 billion years ago in a process colloquially known as the “Big Bang”.
After its initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles. Scientists presently accept the existence of 17 types of subatomic particle. These are known as the “Standard Model of Elementary Particles”.
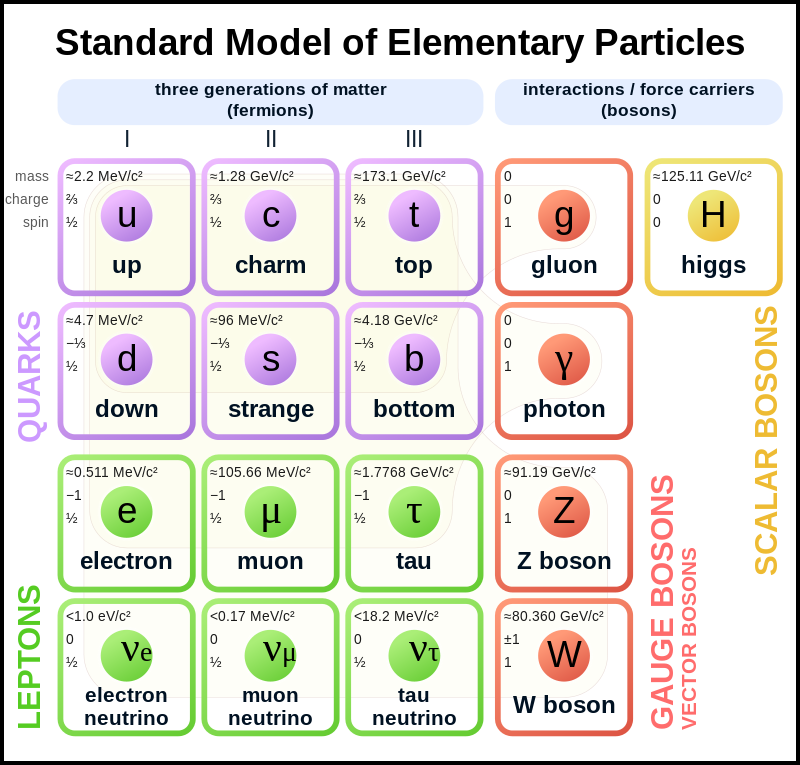
Why the Big Bang should have produced these 17 types of particle is not known, but these particles have the potential within themselves to enable the creation of everything within the Universe that can be created including all living matter, and all machine matter.
This process began with quarks and gluons combining to form protons and neutrons. The protons and neutrons then combined in various proportions to create atomic nuclii. These nuclii combined with electrons to create atoms.
Initially the Big Bang created mostly hydrogen atoms (symbol H, atomic Number 1) a little helium (symbol He, Atomic Number 2), and a tiny proportion of lithium (symbol Li, Atomic number 3). Not much chemistry can be done with just hydrogen, helium and lithium!
But these elements have mass, and mass causes gravitational attraction, which brought together the clouds of hydrogen, helium and lithium together to form stars. As stars grew they started to produce nuclear fusion within themselves. Within this hot and dense environment the conditions created heavier elements by the process of nuclear synthesis. By this method the stars created new elements up to iron (symbol Fe, Atomic Number 56 ). As stars exploded or disintegrated these elements were distributed around the universe.
But on planet Earth there are 94 naturally occurring chemical elements. These heavier elements have been produced by the hotter and more dense conditions inside supernovea. The full list of known chemical elements is shown in the attached Periodic Table. With the 94 native chemical elements plus several created by humanity there is scope for lots of chemistry.
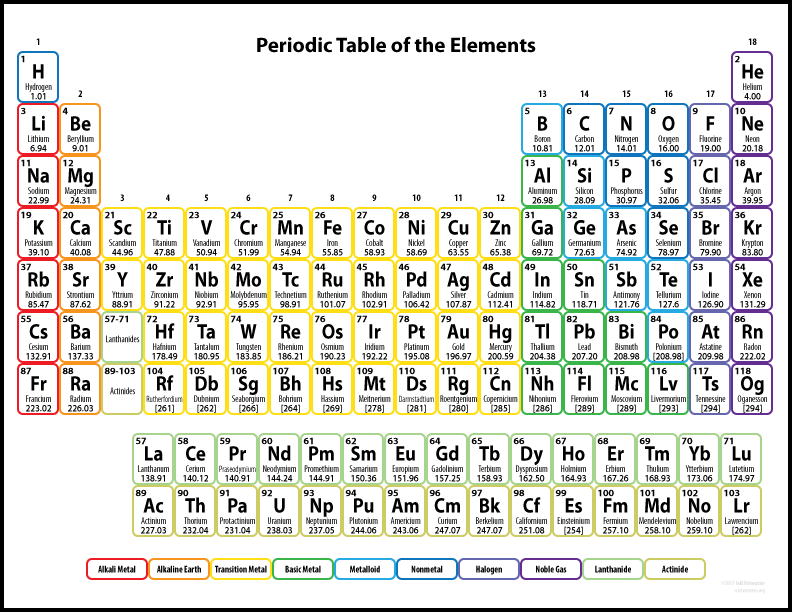
Within this list of chemical elements, there exists one element that is special importance in the chemistry of biological living things. This is carbon, (symbol C, Atomic Number 6). Carbon has the special property of being able form a vast number of organic compounds with elements including hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and the unique property of being able to create a near infinity of different organic chemical molecules. For example, every animal that has ever existed has had a DNA molecule that is unique to that particular animal. Carbon organic molecules can be extremely big comprising thousands of atoms.
Carbon is the essential component of all biological living things on the Earth. Without the existence of carbon with these special propereties there could be no biological abiogenesis, and hence no intelligent life on Earth. These exceptional properties of carbon is yet another example of inexplicable happenings on the progression towards the existence of biological life.
So how and when was biological life on Earth created? Paleontologists are reasonably confident of the timescale, it occurred around 4000 million years ago.
But there is no comprehensive detailed scientific hypothesis regarding the transition from non-living to living entities. Neither have scientists been able to create vital steps in the artificial creation of life. A simple path for the stages of abiogenesis is as follows:
The planet Earth was formed about 4500 Million years ago (Mya). Life began to appear in the sea about 4000 Mya. The first living organisms were prokaryotes (single cell creatures with a surface membrane, but no nucleus), and single cell eukaryotes (with cell nucleus), from about 2200Mya. Multcellular eukaryotes began in the sea about 1600 MYA . The earliest land plants date from about 580 Mya, and land animals from 500 Mya.
The present position in the taxonomic classification of life on Earth puts all living matter into three “Kingdoms”, these are Plants, Animals and Fungi. This classification does not include organisms too small to see with the naked eye, such as microbes, bacteria, viruses, etc.
Animals are distinct from plants and fungi in many ways, but one way is that animals alone have a nervous system comprising neurons. It is neurons that give animals the ability to have coordinated movement, to think, and to have consciousness and intelligence. It is neurons that collect information from the senses such as touch, vision, hearing, taste, smell, and transmit this information to the brain, neurons that process that information within the brain, and neurons that control muscles and movement. The white thread-like data channels throughout the body that we call “nerves”, are actually the axons of neurons.
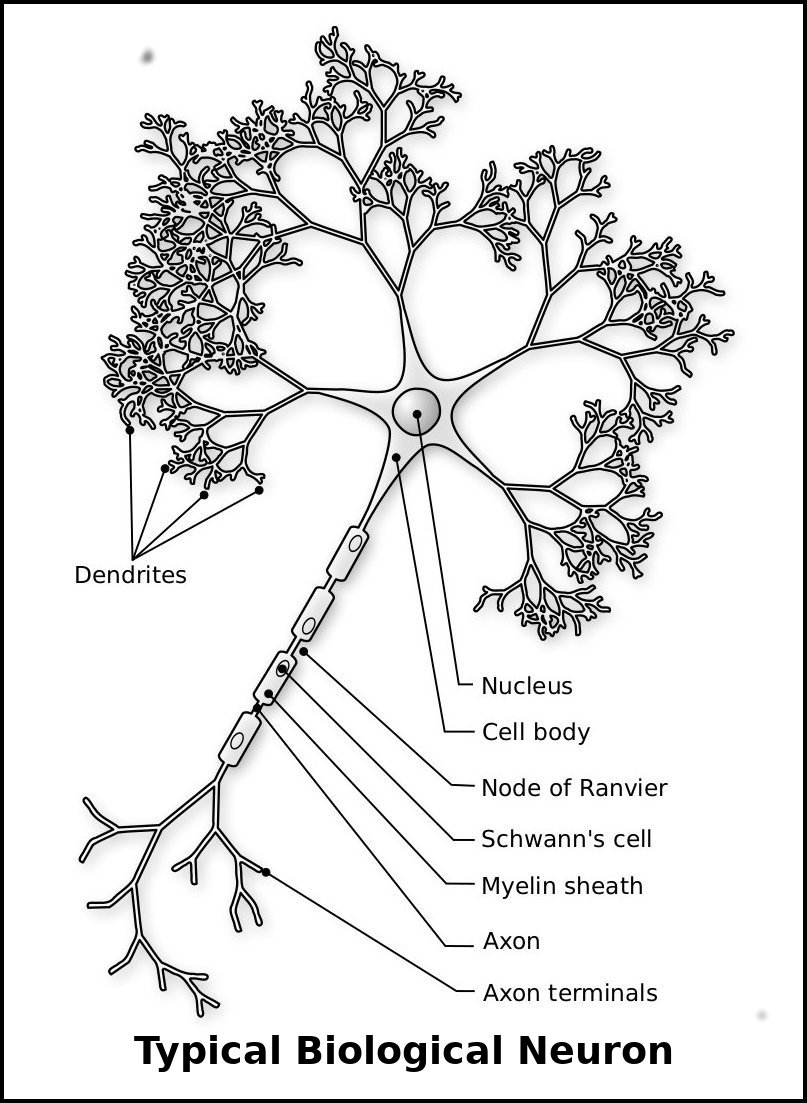
The animal that has found its way to the top of the evolutionary tree, and the apex predator here on the Earth is Homo sapiens, the human being. It is a puny animal that has no bodily weapons such as sharp teath and claws and that can’t even run very fast. It has achieved its top position by having great intelligence, an amazingly effective verbal language, and dextrous hands. These qualities are entirely due to the neurons of its nervous system.
But has the evolutionary progress of human beings peaked, and is the physical and mental qualities of the human species now in decline? Is this decline hidden by the continued growth of knowledge? We no longer breed from our best and strongest. The fastest breeding, and hence backwards evolution, now comes from within religious groups, and poverty-stricken communities.
A recent development in Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the application of neurons. These work on the same principle as biological neurons. The impressive recent steps in AI, such as Deep Learning, image recognition, Natural Language Processing, ChatJPT, rely on neurons.
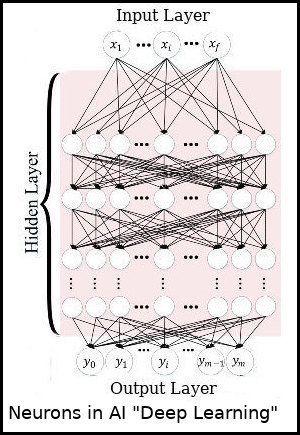
As biological creatures and AI programs share the same neuronal technology, is it not logical that anything biologincal organisms can do, can also be done in principle by machines?
We are not there yet, but AI with neuronal content only began a few decades ago. It is early days yet. Animals have been evolving their neuronal systems for 500,000,000 years. The human being with its intelligent neuronal system has been in existance for about 500,000 years.
Although the evolution of human being may have peaked and now be in decline, the evolution of thinking machines has hardly started. They can carry on when we have gone.
Keith Hayward
23 April 2024